Making Sense of Your Property Tax Statement
Tax bills are mailed annually in mid-December. The following information will help to understand the different sections of the tax statement.
The image below shows a tax statement from 2024. This is a sample tax bill from the state of Wisconsin. Each municipality bill might look a little different, but the same general information is provided. Each red letter corresponds to a description below the image. A definition of terms can be found at the end of the document.
Please note an important piece of information is not included on your property tax bill – the mill rate. The mill rate is the tax rate per $1000 of estimated fair market value. The Edgerton School District mill (levy) rate is currently $7.86.
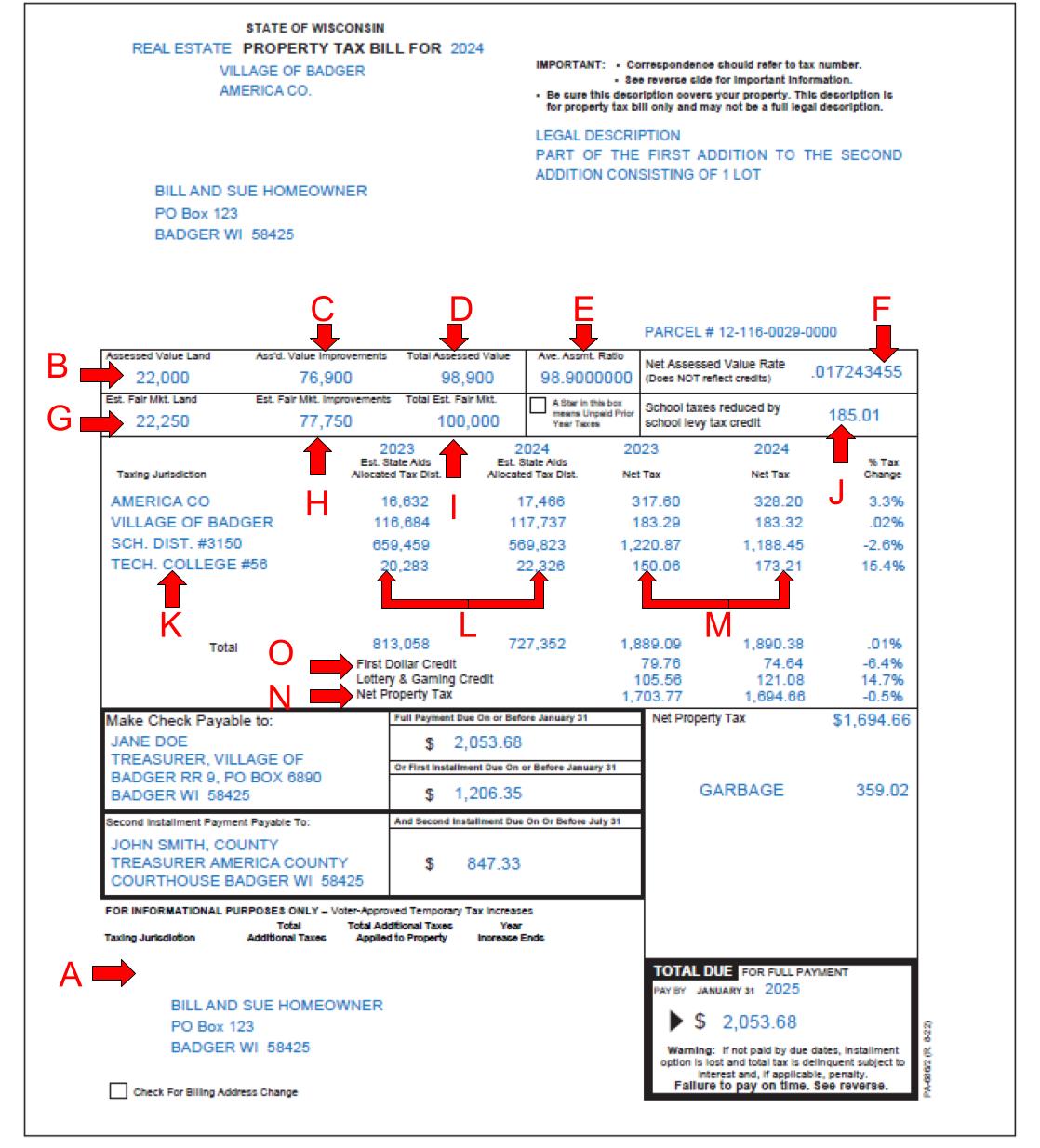
(A) Referendum/Resolution Reminder: State law requires that the items listed below are displayed on Wisconsin property tax bills for each county, municipality, school district and technical college that has a temporary change in tax levy approved after December 31, 2014, by referendum or resolution (for towns with a population under 3,000). This is not a special assessment for any individual jurisdiction listed on the bill.
(B) Assessed Value Land: The value of taxable land, as determined by the assessor for the purpose of taxation.
(C) Assessed Value Improvements: The value of taxable buildings, as determined by the assessor for the purpose of taxation.
(D) Total Assessed Value: The total value of land and buildings, as determined by the assessor for the purpose of taxation. This figure is the sum of (B) and (C) and it may be higher or lower than the current market value of the property. This is multiplied by the net assessed value rate (tax rate) to determine the amount of tax that each property owner must pay.
(E) Average Assessment Ratio: The average assessment ratio is determined by the Wisconsin
Department of Revenue and is used in calculating the estimated fair market value shown on the tax bill. The assessed value divided by the average assessment ratio = estimated fair market value.
For example, if the assessment of a parcel of land, which sold for $150,000 (fair market value) was $140,000, the assessment ratio is said to be 93% (140,000 divided by 150,000).
(F) Net Assessed Value Rate (Tax Rate): The tax rate is determined by dividing the amount of the tax levy — that is, the total amount that is taxed in the entire district — by the total assessed value of all property in the district. The tax rate is then multiplied by the total assessed value to determine the amount of tax that each property owner must pay.
(G) Estimated Fair Market Land: This figure is the assessed value land figure (B) divided by the average assessment ratio (E).
(H) Estimated Fair Market Improvements: This figure is the assessed value improvements figure (C) divided by the average assessment ratio (E).
(I) Total Estimated Fair Market Value: This figure is the sum of the estimated fair market land figure (G) and the estimated fair market improvements figure (H).
(J) School Levy Tax Credit: The school levy tax credit is a credit that is paid to municipalities, not the school district. It issues revenues back to the public in an effort to offset property taxes. This credit is automatically applied to all properties that qualify. It is funded using income, sales and excise taxes.
Despite the fact that these funds do not go to schools, the state considers these dollars part of its commitment to education. School levy tax credits are distributed based on each municipality’s share of statewide levies for school purposes. These amounts are decided based on the value of an individual property as a percentage of the district’s total value.
(K) Taxing Jurisdiction: Any entity authorized by law to levy taxes on property located within its
boundaries. This includes the state, the city (or other local government), the county, the school district, and/or the local technical college.
(L) State Aid: This shows the revenue received from the state for each jurisdiction, for this and the prior year.
(M) Information from Prior Years: This shows the taxes due for each jurisdiction. For comparison, the figures for the prior year are listed with the percent change.
(N) Net Property Tax: This figure is the total property tax minus the lottery and gaming credit, described below.
(O) First Dollar Credit and Lottery and Gaming Credit: Like the School Levy Tax Credit, the First Dollar Credit issues revenues back to the public to offset property taxes. This money does not go to schools, although the state considers it part of its commitment to education. It should be automatically applied to all qualifying properties.
The Lottery and Gaming Credit is a property tax credit, which is provided by the State from its lottery and gaming revenues. The lottery and gaming credit is determined in November of each year and depends on the revenue gained from lotteries, pari-mutuel on-track betting, and bingo for the year. In most cases, the credit is applied automatically.
Definition of Terms
The following terms are used on tax bills, in this document and in other written material about property taxes.
Assessed Value: The value that is assigned to property by the assessor for the purpose of taxation.
Assessment Ratio: The average assessment ratio is provided by the Wisconsin Department of Revenue and is used in calculating the estimated fair market value shown on tax bills. Assessed value is divided by the average assessment ratio to get the estimated fair market value.
Equalized Value: This is the estimated value of all taxable real and personal property in the district. The value used is the market value, which is the most probable selling price.
Fair Market Value: This is the real market value of a property. In other words, it is the price for which a property would be sold by a willing seller to a willing buyer, under normal market conditions.
Levy: The total amount of property taxes imposed by a taxing jurisdiction.
Taxation District: A city, village, or town. If a city or village lies in more than one county, this is the portion of the city or village which lies within each county.
Taxing Jurisdiction: Any entity authorized by law to levy taxes on property located within its boundaries. This includes the state, the city (or other local government), the county, the school district, and/or the local technical college.
